Caching is a technique for storing data in memory so that it can be accessed more quickly. This can be a great way to improve the performance of your NestJs application.
There are many different caching solutions available, but one of the most popular is Redis. Redis is an open-source in-memory data structure store that can be used as a cache.
In this article, I will show you how to use Redis to cache MongoDB data in your NestJs application.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following:
- Node.Js
- A NestJs application
- A Redis server
- Some NestJs and 3rd party dependencies
Setup a NestJs application
The first step is to setup a NestJs application. If you already have one, skip the step. Follow the article here for a step-by-step NestJs application setup. Or you can run the command below:
1 2 3 4 | npm i -g @nestjs/cli nest new nest-test |
Installing the Dependencies
Once you have all of the prerequisites installed and setup, you can install the dependencies using the following command:
1 2 3 | npm install @nestjs/cache-manager cache-manager-redis-yet cache-manager |
Configure the Cache
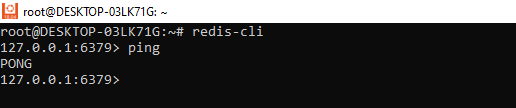
Check the Redis is configured properly and working.
Go to command line where Redis is setup and run redis-cli command. It will connect you to Redis server. Now hit ping command. You will get back PONG from Redis server.
Now configure the Redis Cache in NestJs application. Here is an example of how to configure the cache:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // app.module.ts import { Module } from '@nestjs/common'; import { UsersModule } from './users/users.module'; import { CacheModule } from '@nestjs/cache-manager'; import { redisStore } from 'cache-manager-redis-yet'; @Module({ imports: [ CacheModule.register({ store: redisStore, host: 'localhost', // Redis Server Host name port: 6379, // Redis Server Port isGlobal: true, // Make it true in case you want to use Redis Cache in other modules like UserModule ttl: 1000 * 60 * 5, // Redis Cache time in milliseconds }), UsersModule, ], controllers: [], }) export class AppModule {} |
store: PassredisStoreas you want your data to be stored in Redis Serverhost: Redis Server Host Nameport: Redis Server PortisGlobal: Passtruein case you want to use Redis Caching in other modulesttl: Time in milliseconds. I have put 5 minutes. My cache will be removed from Redis Server after 5 minutes of creation.
Using Redis Cache in NestJs
Once the cache is configured, we can start using it.
Inject the Cache class from cache-manager package.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | import { CACHE_MANAGER } from '@nestjs/cache-manager'; import { Cache } from 'cache-manager'; constructor(@Inject(CACHE_MANAGER) private cacheManager: Cache) {} |
Here is an example of how to use the cache in a controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | // users.controller.ts import { Controller, Get, Inject } from '@nestjs/common'; import { UsersService } from './users.service'; import { User } from './user.model'; import { CACHE_MANAGER } from '@nestjs/cache-manager'; import { Cache } from 'cache-manager'; @Controller('users') export class UsersController { constructor( private readonly userService: UsersService, @Inject(CACHE_MANAGER) private cacheManager: Cache, ) {} @Get() async findAll(): Promise<User[]> { const usersCache = <User[]>await this.cacheManager.get('users'); if (usersCache && usersCache.length > 0) return usersCache; const users = await this.userService.findAll(); await this.cacheManager.set('users', users); return users; } } |
Here is an example of how to use redis cache using NestJs decorator in a controller:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | // users.controller.ts import { Controller, Get, UseInterceptors } from '@nestjs/common'; import { UsersService } from './users.service'; import { User } from './user.model'; import { CacheInterceptor, CacheKey } from '@nestjs/cache-manager'; @Controller('users') export class UsersController { constructor(private readonly userService: UsersService) {} @Get() @UseInterceptors(CacheInterceptor) @CacheKey('users') // I have used `users` key. You can use any key as per your code. async findAll(): Promise<User[]> { return await this.userService.findAll(); } } |
Redis Cache Expiration Time (TTL)
In the example above, I have used global TTL for all the redis keys in app.module.ts file. However you can override the value depending upon the use case in any controller function or at controller level.
Here is an example of how to use Redis TTL in NestJs controller using a decorator:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | // users.controller.ts import { CacheTTL, Controller, Get, UseInterceptors } from '@nestjs/common'; import { UsersService } from './users.service'; import { User } from './user.model'; import { CacheInterceptor, CacheKey } from '@nestjs/cache-manager'; @Controller('users') export class UsersController { constructor(private readonly userService: UsersService) {} @Get() @UseInterceptors(CacheInterceptor) @CacheKey('users') @CacheTTL(10 * 60 * 1000) // Use the decorator here to override global TTL value for ex. 10 minutes async findAll(): Promise<User[]> { return await this.userService.findAll(); } } |
Import CacheTTL from @nestjs/common module. Use CacheTTL decorator just above to a controller function or even at controller level. Pass time in milliseconds. In my example above I have passed 10 minutes.
Check Redis Cache values
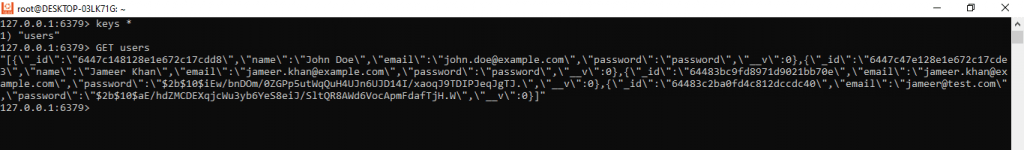
Check the Redis Cached values by the custom key. I have used users as key to store my users data. Here is how to check values:
Use keys * to get all the keys stored in Redis server. Use GET <key name> to get the value of a particular key.
Conclusion
Caching is a great way to improve the performance of your NestJS application. In this article, we showed you how to use Redis to cache MongoDB data in your NestJS application.
Checkout some more articles on NestJs here: