NestJs is a powerful framework for building server-side applications with Node.js. It provides a wide range of features and tools that help developers to build scalable, maintainable, and robust applications. In this article, we will explore some advanced techniques in NestJs, including logging, and error handling.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
Let’s start diving into NestJs advanced techniques to implement Logging, and Error Handling with its in-built decorators and packages.
Logging
Logging is an essential technique for debugging and monitoring your application. It involves recording messages or events that occur during the execution of your application.
NestJs provides built-in support for logging using various logging providers such as Winston, Bunyan, and others. For example, to use Winston as a logging provider, you can install the @nestjs/platform-winston package and add the following code to your application:
Before implementing the code, install the following modules:
1 2 3 | npm install nest-winston winston |
Update the app.module.ts file with the following codes:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | // app.module.ts import { Logger, Module } from '@nestjs/common'; import { WinstonModule } from 'nest-winston'; import * as winston from 'winston'; @Module({ imports: [ WinstonModule.forRoot({ transports: [ new winston.transports.Console({ format: winston.format.combine( winston.format.timestamp(), winston.format.colorize(), winston.format.printf((info) => `${info.timestamp} ${info.level}: ${info.message}`), ), }), ], }), ], }) |
This code registers Winston as a logging provider with a console transport. You can then use the logger instance to log messages:
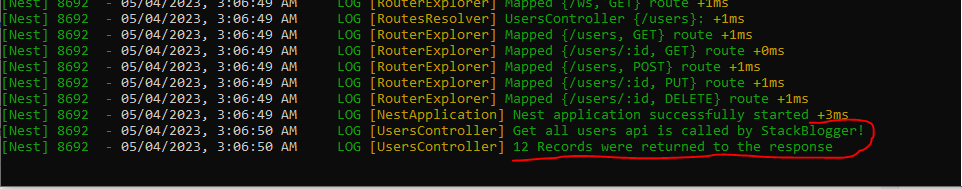
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | // products.controller.ts import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller('products') export class ProductsController { private readonly logger = new Logger(ProductsController.name); @Get() async findAll(): Promise<Product[]> { this.logger.log('Get all products api is called by StackBlogger!'); // Retrieve products from the database const products = await this.productsService.findAll(); this.logger.log(`${products.length} Records were returned to the response`); return products; } } |
In this example, the findAll() method logs a message using the logger instance.
Error Handling
Error handling is an essential technique for handling errors that occur during the execution of your application. It involves catching and handling errors in a way that prevents your application from crashing or producing incorrect results.
NestJs provides built-in support for error handling using various error handling providers such as the built-in HttpExceptionFilter, which handles HTTP exceptions. For example, to use the HttpExceptionFilter, you can add the following code to your application:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | // http-exception.filter.ts import { Catch, HttpException, ExceptionFilter, ArgumentsHost } from '@nestjs/common'; @Catch(HttpException) export class HttpExceptionFilter implements ExceptionFilter { catch(exception: HttpException, host: ArgumentsHost) { const ctx = host.switchToHttp(); const response = ctx.getResponse(); const status = exception.getStatus(); const message = exception.getResponse() as string; response.status(status).json({ statusCode: status, message, }); } } |
This code defines an HttpExceptionFilter that catches HttpException instances and returns a JSON response with the status code and message.
You can then use the @UseFilters() decorator to apply the filter to a controller or method:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | // products.controller.ts import { Controller, Get, NotFoundException, UseFilters } from '@nestjs/common'; @Controller('products') @UseFilters(HttpExceptionFilter) export class ProductsController { @Get(':id') async findOne(@Param('id') id: string): Promise<Product> { const product = await this.productsService.findOne(id); if (!product) { throw new NotFoundException(`Product with ID ${id} not found`); } return product; } } |
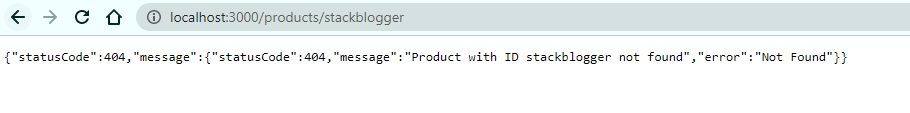
In this example, the findOne() method throws a NotFoundException if the product with the specified ID is not found. The HttpExceptionFilter catches this exception and returns a JSON response with a 404 status code and message.
Conclusion
In this article, we explored some advanced techniques in NestJs, including logging, and error handling. These techniques can help you to build scalable, maintainable, and robust applications. By using built-in providers and decorators, you can easily implement these techniques in your application.