Angular Material is a high quality UI Components to use as an alternate for Bootstrap or any other UI frameworks. Angular Material provides various components to work with. It has its own set of components like Data Tables, Buttons, Popups, Cards and many more.
More info about Angular is here: Angular Material Official Link
In this article we will learn about Angular Material, Data Table, Data Sources, matColumnDef, Sort and Pagination details. I have used Angular 12 and Angular Material 12.2.8 for this example.
Download the complete code from Github here: Repo Link
Before starting the article, let’s look into some common questions about Angular Material.
What is Angular Material Table?
It is a table that provides mat designed data tables in rows and columns. Its similar to HTML table but with more features and designs. It has its own tags and attributes.
What is DataSource in Angular Material?
A datasource is a combined code to handle data retrieval, sorting, filtering, pagination etc things. It contains all logics to work with a DataTable in Angular Material.
What is matColumnDef in Angular?
It is a column definition in mat-table. It defines the set of cells available for the column in material table.
Let’s start the article.
Sit tight! You are going to start a pretty big tutorial 🙂
Create Angular Material DataTable
Add Material into your Angular project
ng add @angular/material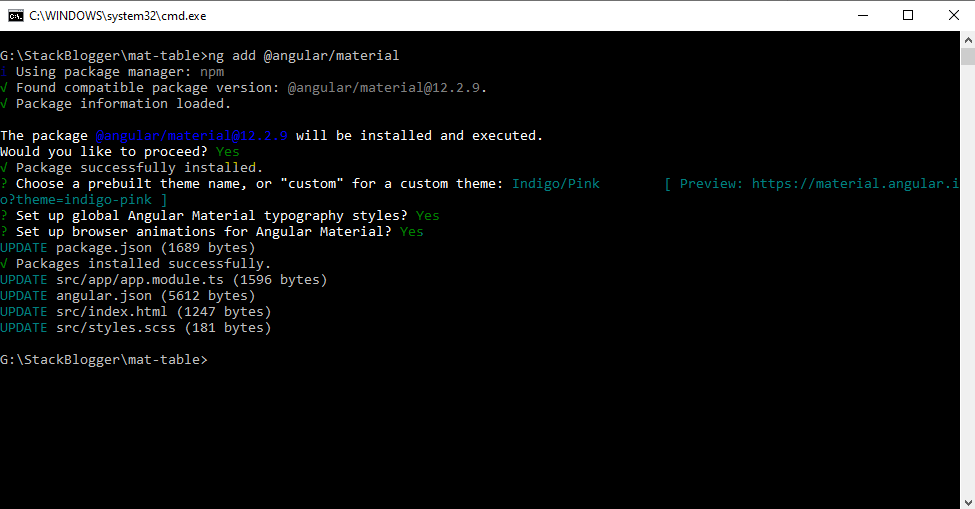
Import Table Module
Import the material modules into app.module.ts file (or any other file in case you are using a shared module file). As we need to implement the sorting as well so I am importing the MatSortModule along with MatCardModule (Card Module will make the UI a little better).
import { MatTableModule } from '@angular/material/table';
import { MatSortModule } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { MatCardModule } from '@angular/material/card';
@NgModule ({
imports: [
MatTableModule,
MatSortModule,
MatCardModule,
// other modules here
]
})
class AppModule {}Create a Service file
Next we have to create a app.service.ts file with getSampleData method. I am using Github Search API to fetch the data. You can replace it with your actual API.
import { Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Observable } from "rxjs";
import { GithubApi } from "./table/table.component";
import { SortDirection } from "@angular/material/sort";
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
constructor(private httpClient: HttpClient) {
}
getSampleData(sort: string, order: SortDirection, page: number): Observable<GithubApi> {
return this.httpClient.get<GithubApi>(`https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=repo:angular/components&sort=${sort}&order=${order}&page=${page + 1}`);
}
}Create Component and Consume API
import { AfterViewInit, Component, ViewChild } from '@angular/core';
import { MatSort } from '@angular/material/sort';
import { of } from 'rxjs';
import { startWith, switchMap, catchError, map } from 'rxjs/operators';
import { AppService } from '../app.service';
export interface GithubApi {
items: GithubIssue[];
total_count: number;
}
export interface GithubIssue {
created_at: string;
number: string;
state: string;
title: string;
}
@Component({
selector: 'app-table',
templateUrl: './table.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./table.component.scss']
})
export class TableComponent implements AfterViewInit {
displayedColumns: string[] = ['created', 'state', 'number', 'title'];
data: GithubIssue[] = [];
@ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort;
constructor(private appService: AppService) { }
ngAfterViewInit() {
// If the user changes the sort order, reset back to the first page.
this.sort.sortChange.subscribe(() => 0);
this.sort.sortChange
.pipe(
startWith({}),
switchMap(() => {
return this.appService!.getSampleData(this.sort.active, this.sort.direction, 0)
.pipe(catchError(() => of(null)));
}),
map(data => {
if (data === null) {
return [];
}
return data.items;
})
).subscribe(data => this.data = data);
}
}Code Explanation: Two interfaces are used as Models- GithubApi and GithubIssue. @ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort; is used to capture the sort click from UI. displayedColumns is used to hold the array of string values to bind Header Dynamically.
Note: We need to use ngAfterViewInit instead of ngOnInit because we need to capture matSort from UI. If we use ngOnInit instead of ngAfterViewInit then it will throw following error:
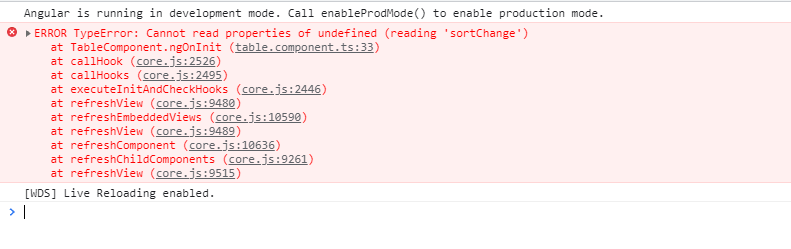
Next we need to capture sortChange on matSort. startWith is used to know when subscription has occurred on an existing observable. switchMap is used to switch to the new observable when sort is clicked before completing its previous request. map is used to check whether response is null. If yes then return blank array so that UI can not complain about null data error.
Create Template and bind Mat Data Table
<mat-card class="example-card">
<mat-card-title>Mat DataTable</mat-card-title>
<mat-card-content>
<div class="example-container mat-elevation-z8">
<div class="example-table-container">
<table mat-table [dataSource]="data" class="example-table" matSort matSortActive="created"
matSortDisableClear matSortDirection="desc">
<!-- Number Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="number">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef>#</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.number}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- Title Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="title">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef>Title</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.title}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- State Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="state">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef>State</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.state}}</td>
</ng-container>
<!-- Created Column -->
<ng-container matColumnDef="created">
<th mat-header-cell *matHeaderCellDef mat-sort-header disableClear>
Created
</th>
<td mat-cell *matCellDef="let row">{{row.created_at | date}}</td>
</ng-container>
<tr mat-header-row *matHeaderRowDef="displayedColumns"></tr>
<tr mat-row *matRowDef="let row; columns: displayedColumns;"></tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</mat-card-content>
</mat-card>Run the app and check view
Now its time to run the app and check whether we have done things right. You will see following output:
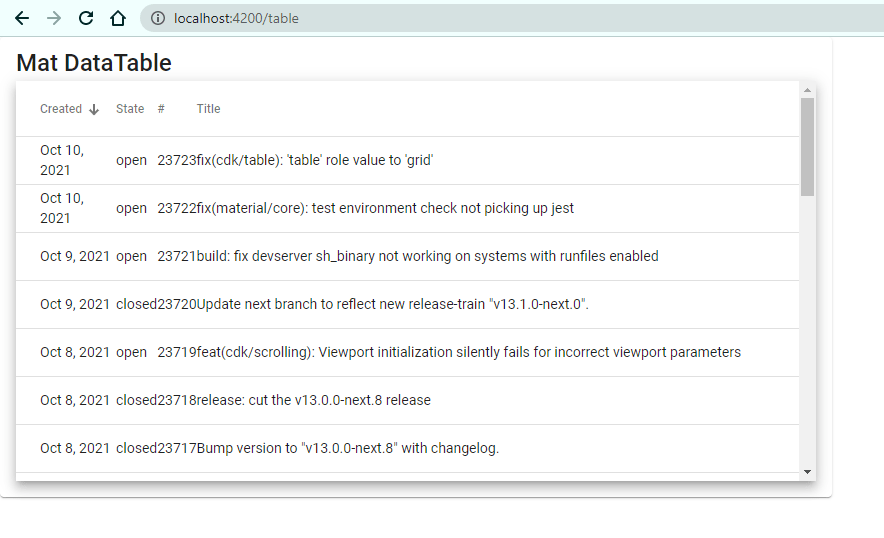
You will get your Material Data Table working with Dynamic Header, Rows and Sorting functionalities. Nice right!
Our Angular Material Dynamic Data Table is complete with Sorting. Its time to implement Searching into it.
Searching in Angular Material Data Table
The next thing we are going to implement is: Server Side Searching in Material Data Table.
Update getSampleData method
Modify your getSampleData file inside app.service.ts to accept a 4th parameter, q. We will pass searchTerm in the 4th parameter.
getSampleData(sort: string, order: SortDirection, page: number, q: string): Observable<GithubApi> {
return this.httpClient.get<GithubApi>(`https://api.github.com/search/issues?q=${q}&sort=${sort}&order=${order}&page=${page + 1}`);
}Update Component
displayedColumns: string[] = ['created', 'state', 'number', 'title'];
data: GithubIssue[] = [];
@ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort;
term$ = new BehaviorSubject<string>('');
constructor(private appService: AppService) { }
ngAfterViewInit() {
// If the user changes the sort order, reset back to the first page.
this.sort.sortChange.subscribe(() => 0);
merge(this.sort.sortChange, this.term$.pipe(debounceTime(1000), distinctUntilChanged()))
.pipe(
startWith({}),
switchMap((searchTerm) => {
return this.appService!.getSampleData(this.sort.active, this.sort.direction, 0, (searchTerm && typeof searchTerm == 'string') ? searchTerm.toString() : 'repo:angular/components')
.pipe(catchError(() => of(null)));
}),
map(data => {
if (data === null) {
return [];
}
return data.items;
})
).subscribe(data => this.data = data);
}Here I have used RxJS merge operator to merge Sort and Search subscriptions together. debounceTime is used to wait for 1 sec when user types. distinctUntilChanged is used to call search API only if your search query is different than previous.
(searchTerm && typeof searchTerm == 'string') ? searchTerm.toString() : 'repo:angular/components'Above condition is used to check whether the search term is string, not Sort (because I have combined search and sort together).
Update template
Include a text box for search.
<input type="text" placeholder="Search a text" (input)="term$.next($any($event.target).value)"> Term-{{term$|async}}Run the page again and go to browser. Your output will look like this:
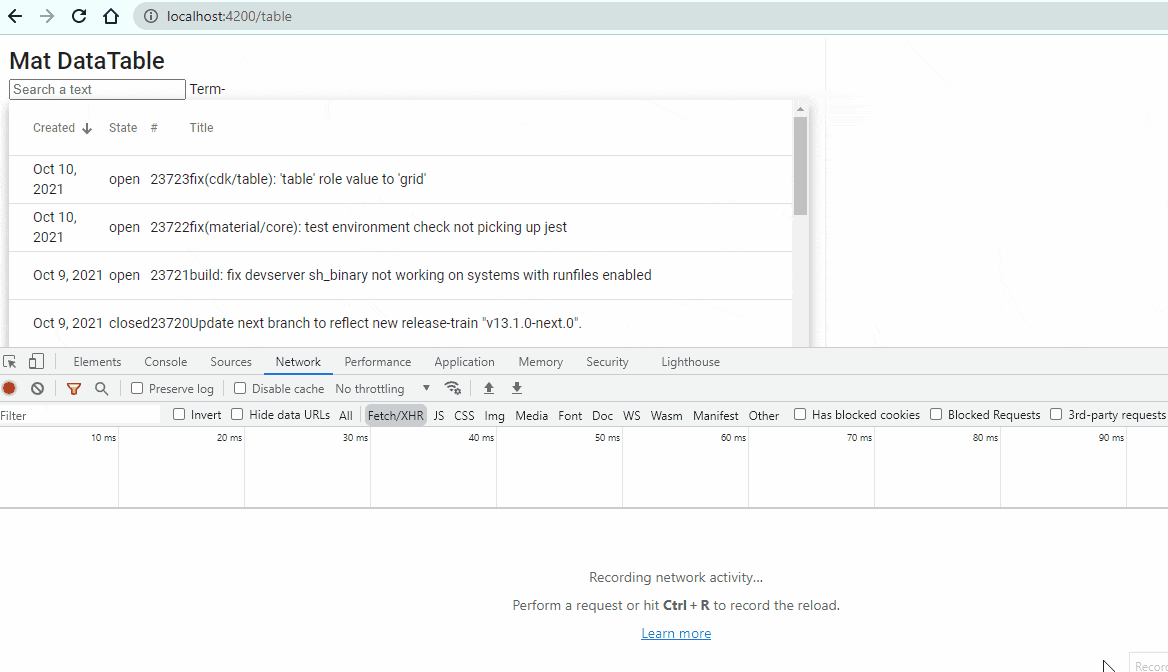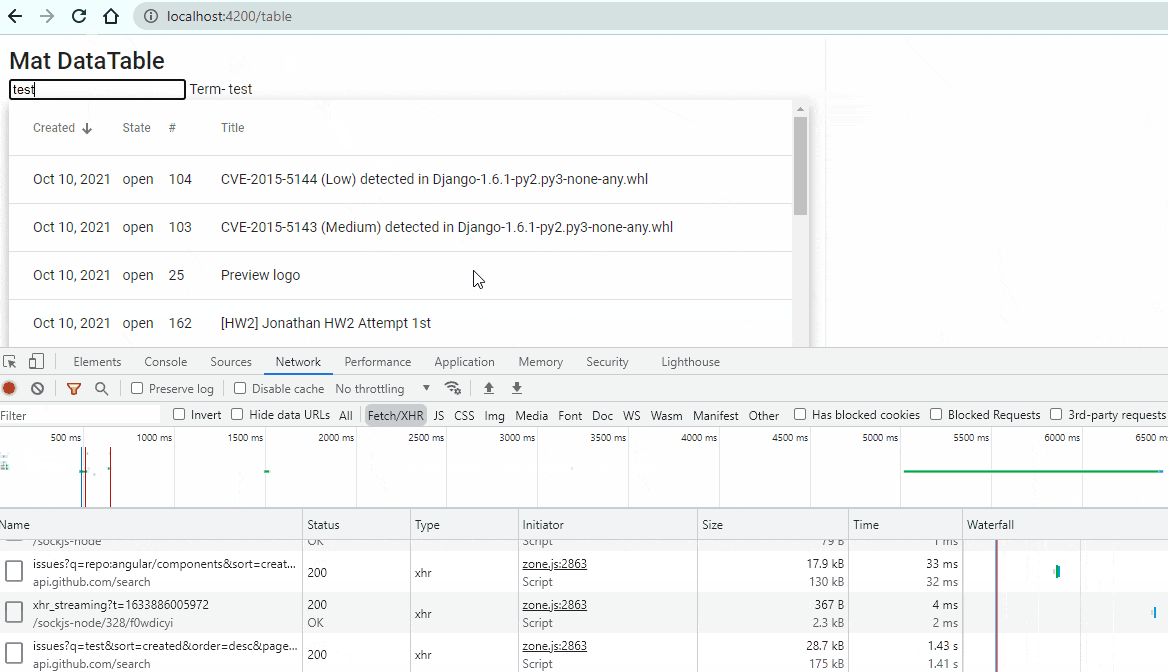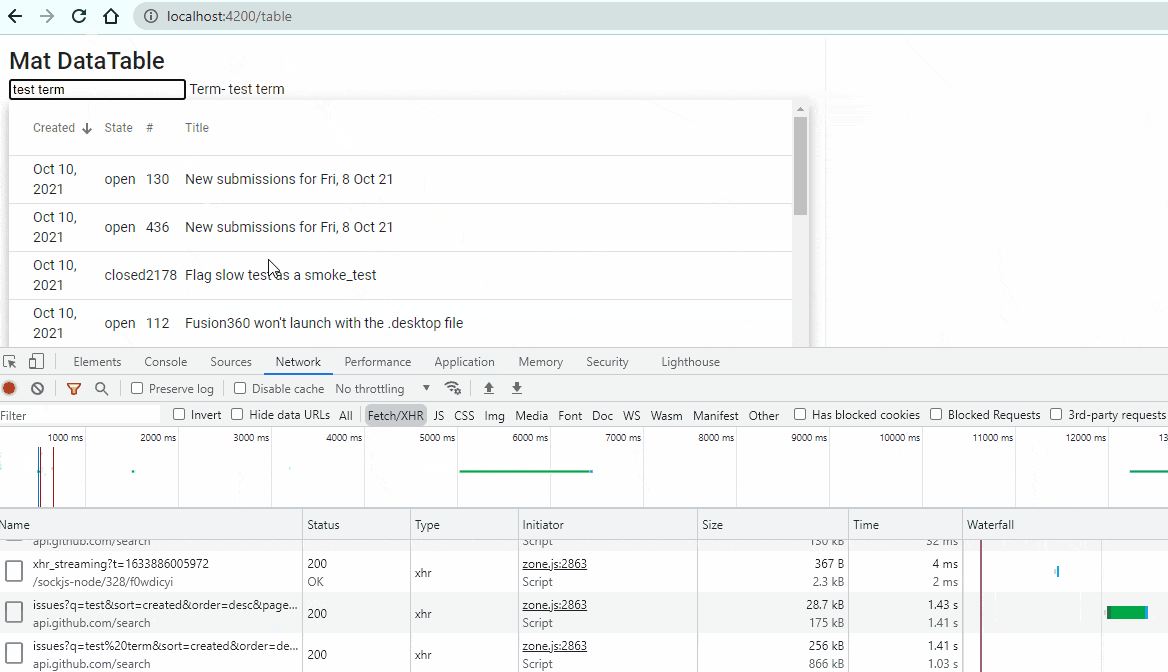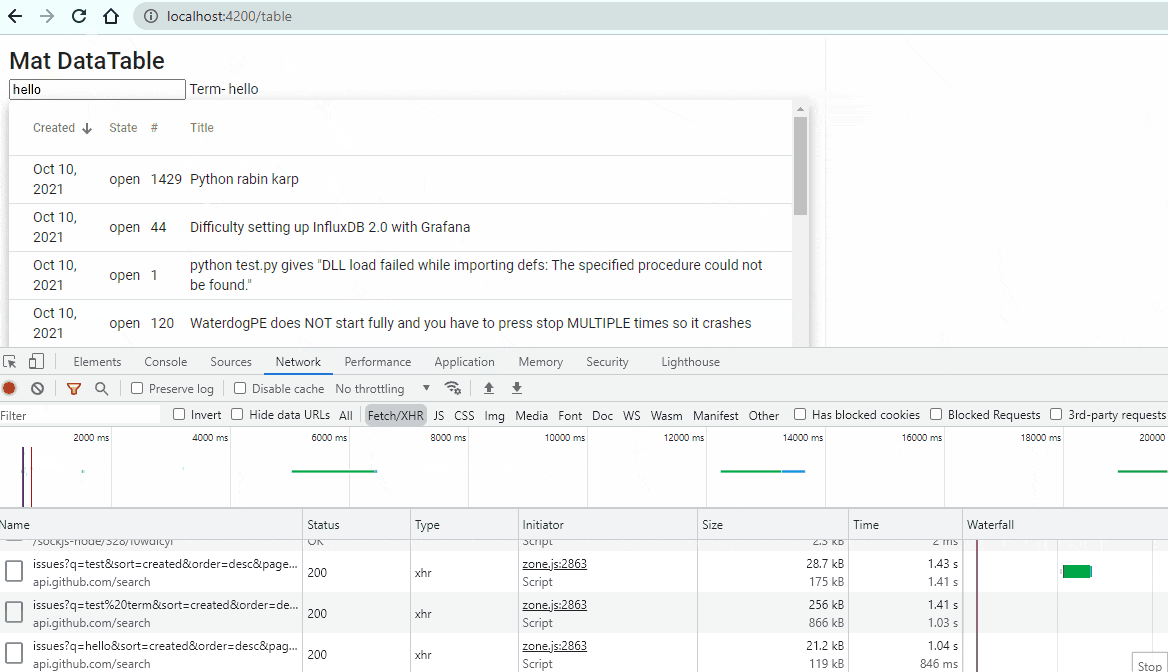
Yayyyy! Your Server Side Search functionality is implement and working properly.
Now the next thing to implement is: Server Side Pagination Functionality
Server Side Pagination Functionality
Pagination is the way to display data page by page instead of all at one page. Server Side Pagination improves website speed. Check 5 Best Ways To Optimize Angular For Scaling
Import Pagination Module
Import Paginator Module in app.module.ts file
import { MatProgressBarModule } from '@angular/material/progress-bar';Update Component for Paging
Update your Component file with below code:
displayedColumns: string[] = ['created', 'state', 'number', 'title'];
data: GithubIssue[] = [];
@ViewChild(MatSort) sort!: MatSort;
term$ = new BehaviorSubject<string>('');
resultsLength = 0;
@ViewChild(MatPaginator) paginator!: MatPaginator;
constructor(private appService: AppService) { }
ngAfterViewInit() {
// If the user changes the sort order, reset back to the first page.
this.sort.sortChange.subscribe(() => this.paginator.pageIndex = 0);
merge(this.sort.sortChange, this.term$.pipe(debounceTime(1000), distinctUntilChanged()), this.paginator.page)
.pipe(
startWith({}),
switchMap((searchTerm) => {
return this.appService!.getSampleData(this.sort.active, this.sort.direction, this.paginator.pageIndex, (searchTerm && typeof searchTerm == 'string') ? searchTerm.toString() : 'repo:angular/components')
.pipe(catchError(() => of(null)));
}),
map(data => {
if (data === null) {
return [];
}
this.resultsLength = data.total_count;
return data.items;
})
).subscribe(data => this.data = data);
}You will notice this.paginator.page is merged with other two Events. This way we don’t need to create any separate click events for Paging. The merge operator will merge all the Events and will emit event if any of those will change its value.
Add Paginator in Template
Add mat-paginator tag in html template.
<mat-paginator [length]="resultsLength" [pagesize]="30" aria-label="Select page of GitHub search results">
</mat-paginator>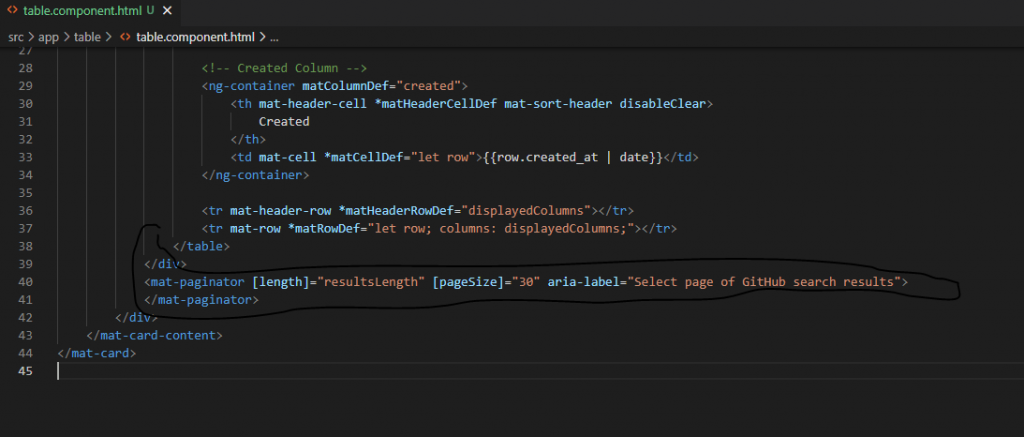
Wow! You are here means you have done pretty big task today 🙂 . Anyways, let’s check the output now.
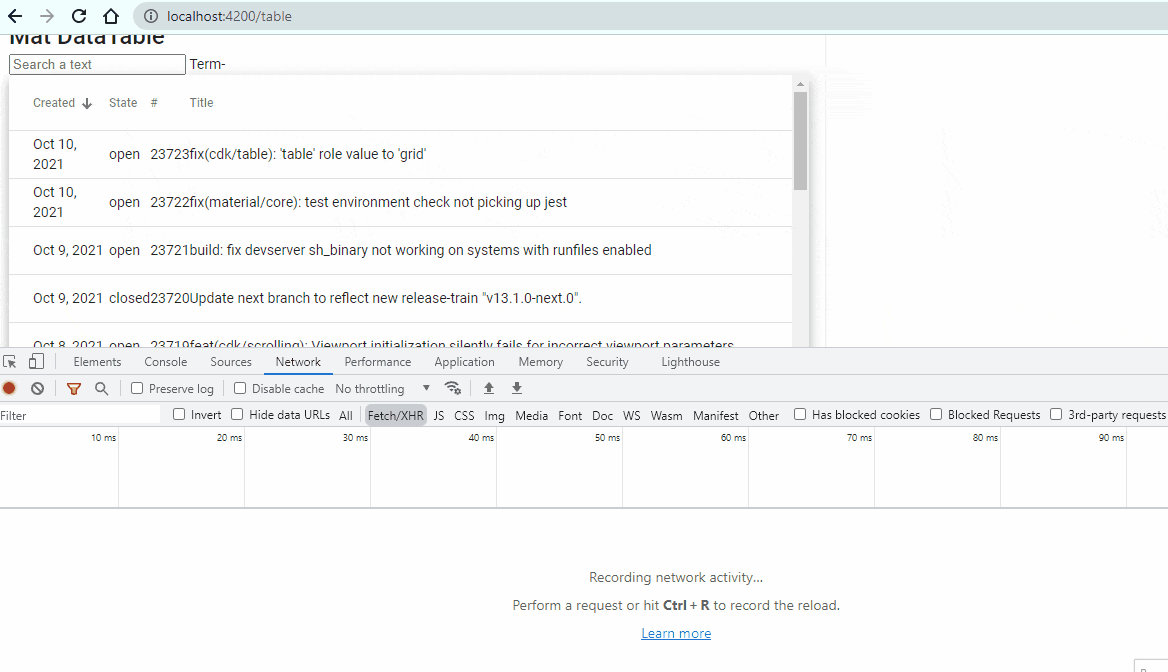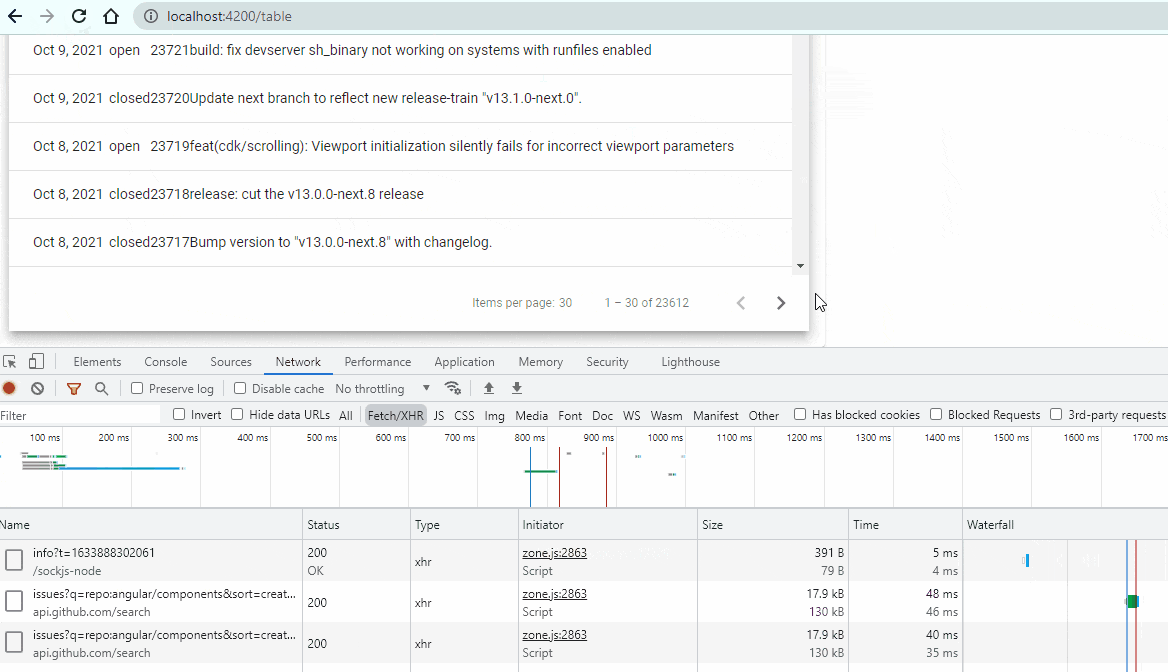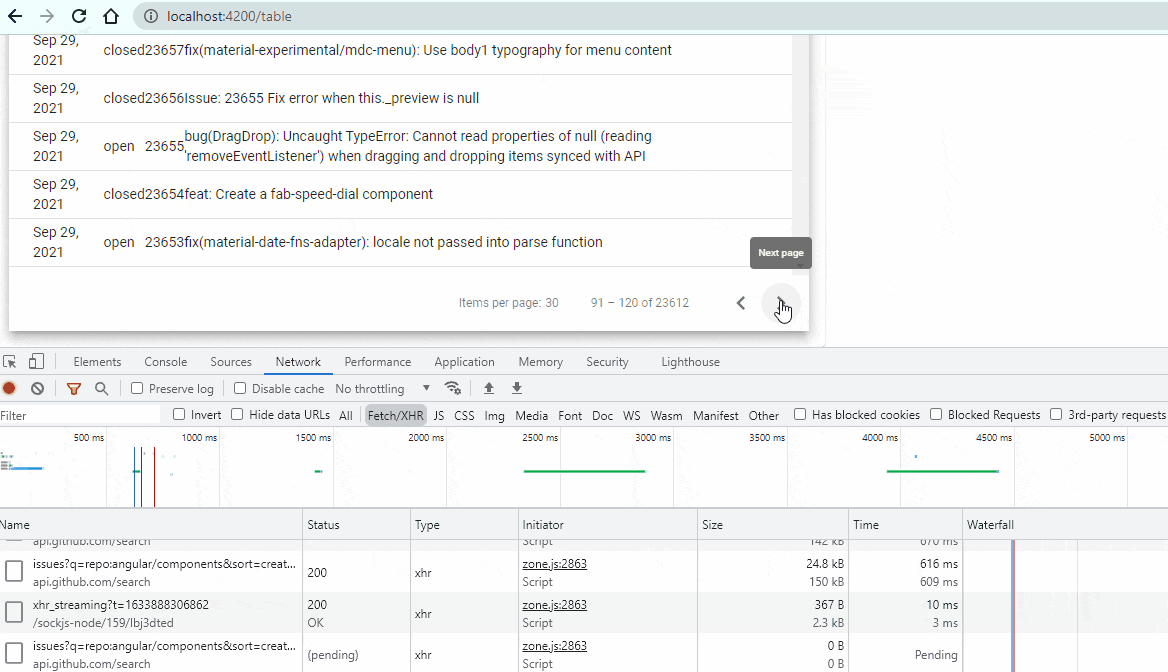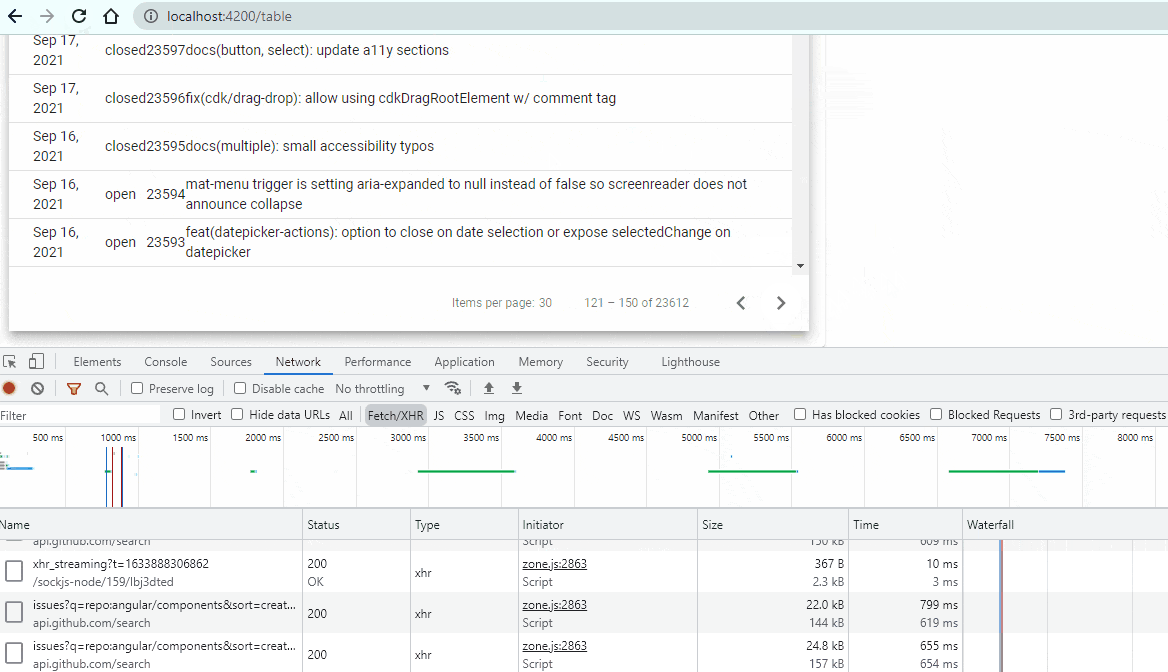
Cool! Our Pagination is working. You did it!!
Conclusion
In this article we learnt:
- Create a Dynamic Angular Material Data Table with Sorting
- Implement Server Side Search in Material Data Table
- Implement Pagination in Material Data Table
Well, that’s all for now. If you liked the article, do share with other programmers.
Download the complete code from Github here: Repo Link
Must Read:
RxJS forkJoin: Definition and Real World Uses
Real World Examples of 5 Common Observable Operators
5 Best Ways To Optimize Angular For Scaling (2021)
7 Best Ways To Improve Angular Code (2021)
5 Great SEO Ideas To Improve Angular Website Ranking